Thursday 30 May 2013
Wednesday 29 May 2013
Bulletin (SB13-147) Vulnerability Summary for the Week of May 20, 2013
Original release date: May 28, 2013
The US-CERT Cyber Security Bulletin provides a summary of new vulnerabilities that have been recorded by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) National Vulnerability Database (NVD) in the past week. The NVD is sponsored by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center (NCCIC) / United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT). For modified or updated entries, please visit the NVD, which contains historical vulnerability information.
The vulnerabilities are based on the CVE vulnerability naming standard and are organized according to severity, determined by the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) standard. The division of high, medium, and low severities correspond to the following scores:
- High - Vulnerabilities will be labeled High severity if they have a CVSS base score of 7.0 - 10.0
- Medium - Vulnerabilities will be labeled Medium severity if they have a CVSS base score of 4.0 - 6.9
- Low - Vulnerabilities will be labeled Low severity if they have a CVSS base score of 0.0 - 3.9
Entries may include additional information provided by organizations and efforts sponsored by US-CERT. This information may include identifying information, values, definitions, and related links. Patch information is provided when available. Please note that some of the information in the bulletins is compiled from external, open source reports and is not a direct result of US-CERT analysis.
| 3s-software -- codesys_gateway-server | Use-after-free vulnerability in the server application in 3S CODESYS Gateway 2.3.9.27 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (daemon crash) or possibly execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-23 | 10.0 | CVE-2013-2781 |
| angusj -- resource_hacker | Heap-based buffer overflow in Resource Hacker 3.6.0.92 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a Portable Executable (PE) file with a resource section containing a string that has many tab or line feed characters. | 2013-05-23 | 9.3 | CVE-2012-6553 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted enof atoms in a movie file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-0986 |
| apple -- quicktime | Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted QTIF file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-0987 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted FPX file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-0988 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted MP3 file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-0989 |
| apple -- quicktime | Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted TeXML file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1015 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted movie file with H.263 encoding. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1016 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted dref atoms in a movie file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1017 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted movie file with H.264 encoding. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1018 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted movie file with Sorenson encoding. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1019 |
| apple -- quicktime | Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via crafted JPEG data in a movie file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1020 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted JPEG data in a movie file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1021 |
| apple -- quicktime | Buffer overflow in Apple QuickTime before 7.7.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted mvhd atoms in a movie file. | 2013-05-24 | 9.3 | CVE-2013-1022 |
| freenac -- freenac | SQL injection vulnerability in deviceadd.php in FreeNAC 3.02 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the status parameter. | 2013-05-23 | 7.5 | CVE-2012-6560 |
| google -- chrome | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2836 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2837 |
| google -- chrome | Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of clipboard data, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2839 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in the media loader in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2013-2846. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2840 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of Pepper resources. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2841 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of widgets. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2842 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of speech data. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2843 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to style resolution. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2844 |
| google -- chrome | The Web Audio implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2845 |
| google -- chrome | Use-after-free vulnerability in the media loader in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2013-2840. | 2013-05-22 | 7.5 | CVE-2013-2846 |
| infotecs -- vipnet_client | Infotecs ViPNet Client 3.2.10 (15632) and earlier, ViPNet Coordinator 3.2.10 (15632) and earlier, ViPNet Personal Firewall 3.1 and earlier, and ViPNet SafeDisk 4.1 (0.5643) and earlier use weak permissions (Everyone: Full Control) for a folder under %PROGRAMFILES%\Infotecs, which allows local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse (1) executable file or (2) DLL file. | 2013-05-22 | 7.2 | CVE-2013-3496 |
| turck -- bl20_programmable_gateway | TURCK BL20 Programmable Gateway and BL67 Programmable Gateway have hardcoded accounts, which allow remote attackers to obtain administrative access via an FTP session. | 2013-05-23 | 10.0 | CVE-2012-4697 |
| a51dev -- activecollab_chat_module | functions/html_to_text.php in the Chat module before 1.5.2 for activeCollab allows remote authenticated users to execute arbitrary PHP code via the message[message_text] parameter to chat/add_messag, which is not properly handled when executing the preg_replace function with the eval switch. | 2013-05-23 | 6.5 | CVE-2012-6554 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0991 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0992 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0993 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0994 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0995 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0996 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0997 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0998 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-0999 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1000 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1001 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1002 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1003 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1004 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1005 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1006 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1007 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1008 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1010 |
| apple -- itunes | WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 11.0.3, allows man-in-the-middle attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors related to iTunes Store browsing, a different vulnerability than other WebKit CVEs listed in APPLE-SA-2013-05-16-1. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-1011 |
| canonical -- telepathy-idle | telepathy-idle before 0.1.15 does not verify (1) that the issuer is a trusted CA, (2) that the server hostname matches a domain name in the subject's Common Name (CN), or (3) the expiration date of the X.509 certificate, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to spoof SSL servers via an arbitrary valid certificate. | 2013-05-21 | 5.8 | CVE-2007-6746 |
| cisco -- ios_xr | Memory leak in the SNMP process in Cisco IOS XR allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory consumption or process reload) by sending many port-162 UDP packets, aka Bug ID CSCug80345. | 2013-05-23 | 5.0 | CVE-2013-1204 |
| elgg -- elgg | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in engine/lib/views.php in Elgg before 1.8.5 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the view parameter to index.php. NOTE: some of these details are obtained from third party information. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6561 |
| elgg -- elgg | engine/lib/users.php in Elgg before 1.8.5 does not properly specify permissions for the useradd action, which allows remote attackers to create arbitrary accounts. | 2013-05-23 | 6.8 | CVE-2012-6562 |
| elgg -- elgg | engine/lib/access.php in Elgg before 1.8.5 does not properly clear cached access lists during plugin boot, which allows remote attackers to read private entities via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6563 |
| emc -- rsa_authentication_agent | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in EMC RSA Authentication Agent 7.1 before 7.1.1 for Web for Internet Information Services, and 7.1 before 7.1.1 for Web for Apache, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 4.3 | CVE-2013-0942 |
| emc -- celerra_control_station | EMC VNX Control Station before 7.1.70.2 and Celerra Control Station before 6.0.70.1 have an incorrect group ownership for unspecified script files, which allows local users to gain privileges by leveraging nasadmin group membership. | 2013-05-20 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-3270 |
| freenac -- freenac | Multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in FreeNAC 3.02 allow remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the (1) comment, (2) mac, (3) graphtype, (4) name, or (5) type parameter to stats.php; or (6) comment parameter to deviceadd.php. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6559 |
| google -- chrome | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 5.0 | CVE-2013-2838 |
| google -- chrome | Race condition in the workers implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 6.8 | CVE-2013-2847 |
| google -- chrome | The XSS Auditor in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 might allow remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 5.0 | CVE-2013-2848 |
| google -- chrome | Multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allow user-assisted remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors involving a (1) drag-and-drop or (2) copy-and-paste operation. | 2013-05-22 | 4.3 | CVE-2013-2849 |
| heaventools -- pe_explorer | Heap-based buffer overflow in HeavenTools PE Explorer 1.99 R6 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via the size value for a string in the resource section of a Portable Executable (PE) file. | 2013-05-23 | 6.8 | CVE-2012-6558 |
| jspautsch -- firstlastnames | Multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the FirstLastNames plugin 1.1.1 for Vanilla Forums allow remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the (1) User/FirstName or (2) User/LastName parameter to the edit user page. NOTE: some of these details are obtained from third party information. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6556 |
| microsys -- promotic | Directory traversal vulnerability in the PmWebDir object in the web server in MICROSYS PROMOTIC before 8.1.5 allows remote attackers to read arbitrary files via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-23 | 5.0 | CVE-2011-4518 |
| microsys -- promotic | Stack-based buffer overflow in an ActiveX component in MICROSYS PROMOTIC before 8.1.5 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via a crafted web page. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2011-4519 |
| microsys -- promotic | Heap-based buffer overflow in an ActiveX component in MICROSYS PROMOTIC before 8.1.5 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via a crafted web page. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2011-4520 |
| openstack -- keystone | OpenStack Identity (Keystone) Folsom 2012.2.4 and earlier, Grizzly before 2013.1.1, and Havana does not immediately revoke the authentication token when deleting a user through the Keystone v2 API, which allows remote authenticated users to retain access via the token. | 2013-05-21 | 6.0 | CVE-2013-2059 |
| qemu -- qemu | The qemu guest agent in Qemu 1.4.1 and earlier, as used by Xen, when started in daemon mode, uses weak permissions for certain files, which allows local users to read and write to these files. | 2013-05-21 | 6.9 | CVE-2013-2007 |
| redhat -- enterprise_linux | rhn-migrate-classic-to-rhsm tool in Red Hat subscription-manager does not verify the Red Hat Network Classic server's X.509 certificate when migrating to a Certificate-based Red Hat Network, which allows remote man-in-the-middle attackers to obtain sensitive information such as user credentials. | 2013-05-21 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6137 |
| sahotataran -- latestcomment | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the LatestComment plugin 1.1 for Vanilla Forums allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the discussion title. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6555 |
| vercot -- serva32 | Buffer overflow in the TFTPD service in Serva32 2.1.0 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (daemon crash) or possibly execute arbitrary code via a long string in a read request. | 2013-05-20 | 5.0 | CVE-2013-0145 |
| web2py -- web2py | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in static/js/share.js (aka the social bookmarking widget) in Web2py before 2.3.1 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-22 | 4.3 | CVE-2013-2311 |
| xen -- xen | Xen 4.0.x and 4.1.x incorrectly releases a grant reference when releasing a non-v1, non-transitive grant, which allows local guest administrators to cause a denial of service (host crash), obtain sensitive information, or possible have other impacts via unspecified vectors. | 2013-05-21 | 6.9 | CVE-2013-1964 |
| zodiacdm -- aboutme-plugin | Multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the AboutMe plugin 1.1.1 for Vanilla Forums allow remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the (1) AboutMe/RealName, (2) AboutMe/Name, (3) AboutMe/Quote, (4) AboutMe/Loc, (5) AboutMe/Emp, (6) AboutMe/JobTit, (7) AboutMe/HS, (8) AboutMe/Col, (9) AboutMe/Bio, (10) AboutMe/Inter, (11) AboutMe/Mus, (12) AboutMe/Gam, (13) AboutMe/Mov, (14) AboutMe/FTV, or (15) AboutMe/Bks parameter to the Edit My Details page. NOTE: some of these details are obtained from third party information. | 2013-05-23 | 4.3 | CVE-2012-6557 |
| apple -- itunes | Apple iTunes before 11.0.3 does not properly verify X.509 certificates, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to spoof HTTPS servers via an arbitrary valid certificate. | 2013-05-20 | 2.9 | CVE-2013-1014 |
| openstack -- devstack | OpenStack devstack uses world-readable permissions for keystone.conf, which allows local users to obtain sensitive information such as the LDAP password and admin_token secret by reading the file. | 2013-05-21 | 2.1 | CVE-2013-1977 |
| openstack -- keystone | OpenStack Identity (Keystone) Grizzly 2013.1.1, when DEBUG mode logging is enabled, logs the (1) admin_token and (2) LDAP password in plaintext, which allows local users to obtain sensitive by reading the log file. | 2013-05-21 | 2.1 | CVE-2013-2006 |
| rsa -- authentication_agent | EMC RSA Authentication API before 8.1 SP1, RSA Web Agent before 5.3.5 for Apache Web Server, RSA Web Agent before 5.3.5 for IIS, RSA PAM Agent before 7.0, and RSA Agent before 6.1.4 for Microsoft Windows use an improper encryption algorithm and a weak key for maintaining the stored data of the node secret for the SecurID Authentication API, which allows local users to obtain sensitive information via cryptographic attacks on this data. | 2013-05-22 | 2.1 | CVE-2013-0941 |
Monday 27 May 2013
Friday 24 May 2013
Mobile phones, flash disks, are personal gadgets posing online security challenges to businesses
Employers might redesign regulation at work minimizing use of personal devices at work blamed for rise in online insecurity to businesses.
A new study by Cisco networks blames current work lifestyles adopted by employees for the rise of network insecurity in offices.
Security risks in businesses are on the rise because many employees adopt “my way” work lifestyles in which their devices, work and online behavior mix with their personal lives virtually anywhere – in the office, at home and everywhere in between.
Cisco report says the today’s trend towards ‘Bring Your Own Device’ (BYOD) is increasingly impacting IT departments. According to Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG) Research 95 per cent of organizations globally now allow employee-owned devices in some way, shape or form in the workplace.
BYOD does however bring complexity when it comes to security and IT Support. The challenge that the Middle East and Africa will face with BYOD is introducing and managing a solid security strategy.
As more and more employees are using devices for both personal and business activities, the issues with potential loss of confidential company data increases as IT departments are less in control.
Companies in 2013 will have to ensure that devices have business application and data isolated and protected.
Cisco Annual Security Report (ASR) in Middle East and Africa also reveals that the highest concentration of online security threats come from legitimate destinations visited by mass audiences, such as major search engines, retail sites and social media outlets.
According to the report, android malware encounters grew 2,577 percent over last year; however, mobile malware represents only 0.5 percent of total Web malware encounters.
Android malware entered the mainstream consciousness in 2012 with explosive growth and the first documented botnet.
Spam volume in the report dropped 18 percent from 2012 to 2011, with spammers working “banker’s hours” for a 25 percent drop in spam over the weekend. “In 2012, the majority of spam was sent during the workweek – Tuesday was the heaviest spam day of the year,” says the survey.
India is the top source of spam worldwide, with the U.S. moving from sixth in 2011 to second in 2012. Korea, China and Vietnam round out the top five.
The top spoofed brands involve prescription drugs and luxury watches like Rolex and Omega. Cisco says spammers maximize the return on investment of their efforts, targeting real-world events with specific and short-lived campaigns
Tuesday 21 May 2013
Will BlackBerry, Nokia or Amazon Replace Apple or Google?
 With Apple stumbling and Google and Samsung possibly on the outs, there may be an opening in the mobile market for an underdog to make a big move. BlackBerry may have the best shot with its strength among businesses in emerging markets, but Nokia is gaining some traction, and Microsoft has deep pockets. Then there's Amazon, which could corner the phablet market. It's anyone's game.
With Apple stumbling and Google and Samsung possibly on the outs, there may be an opening in the mobile market for an underdog to make a big move. BlackBerry may have the best shot with its strength among businesses in emerging markets, but Nokia is gaining some traction, and Microsoft has deep pockets. Then there's Amazon, which could corner the phablet market. It's anyone's game.
Apple and Google are currently at the top of the mobile device heap, but both companies are vulnerable at the moment. Apple has lost its iconic CEO and appears to be chasing Samsung, and you can't lead by following. Samsung is the dominant player on Android, but Google and Samsung are having relationship problems at the moment. Both have been quietly expressing dissatisfaction with the other.
No other vendor -- except possibly LG or Lenovo -- appears truly ready to replace Samsung should it abandon the platform, but with efforts like Knox, Samsung is increasingly stepping away from the Google Android user experience. Positioning to take the place of either Apple or Google/Samsung should one slip are a) the firm that used to dominate phones, Nokia, backed by Microsoft; b) the firm that used to dominate smartphones, BlackBerry; and c) the most powerful online retailer in the world, Amazon.
I'm going to focus on the strengths and weaknesses that each of these challengers has in aiming for the No. 2 spot and assess how likely any one of them is to replace Apple or Google. I'll close with my product of the week, which is a new phone by BlackBerry, the Q5.
Current Market Share
Android is well ahead of the pack, based on thelatest IDC numbers, but it is estimated that around half of the products running it aren't under Google's control, representing multiple forks in the Android code base.Still even if you cut Android's 75 percent share in half, at 37.5 percent you'd still be more than twice Apple's, which has fallen to 17.3 percent. However, that 37.5 percent is mostly Samsung. Windows Phone passed BlackBerry -- slightly -- for a distant No. 3, and this is virtually all Nokia, but effectively the two platforms are now tied.
The Case for BlackBerry
I spent last week at BlackBerry Live, and I think BlackBerry has the best shot at getting back to its former glory and market leadership for three reasons: 1) It owns its platform -- it doesn't have to partner to succeed; 2) it is focused on business, a segment that the other platform leaders have until recently ignored; and 3) in world where malware is increasing massively for mobile devices, it is the only vendor with a platform designed to be secure from the start.On the other hand, it lags the other players in terms of available resources -- and in a fight like this, resources are very important.
The other interesting advantage that BlackBerry has is that in emerging markets, it is comparatively strong against Apple, the other fully integrated vendor. This was made clear to me at BlackBerry Live, where representatives from those markets dominated. That's largely because BYOD isn't happening in those regions, as employees simply can't afford to buy their own devices. For the most part, where companies still buy, BlackBerry still rules.
I looked at the U.S. Department of Defense, for instance, and while it is conducting trials with Android, iOS, and BlackBerry, the numbers are telling, with around 10K Android, around 40K Apple, and around 500K BlackBerry devices. Where business dominates, BlackBerry rules -- and given an increased focus on security and business, I give BlackBerry the edge.
The Nokia/Windows Combo
Windows Phone is faster moving at the moment, however, based on the IDC numbers. Nokia is winning design awards, has rolled out an aggressive TV campaign targeting both Apple and Samsung, and has a number of desirable features -- like the best camera on a smartphone and inductive charging on some of its lines.It gets financial backing from Microsoft, which still has a financial reserve rivaled only by Apple and Google -- and Apple will be eliminating most of its financial reserve this year to placate pissed-off shareholders. Finally, it is focused on the consumer segment, which is where the segment growth has been coming from since the iPhone launched.
Microsoft has proven to be a mixed blessing in this effort. Nokia's momentum was damaged by rumors that Microsoft had lost faith and was developing its own phone. Nokia has had to constantly reaffirm its commitment to Microsoft.
Windows Phone as a brand appears to have negative implications for most buyers, who connect the name to the Windows 8 desktop platform, which is having teething problems. These drawbacks appear to more than offset the resource advantage Nokia/Microsoft should have and reflect on an ongoing problem with most Microsoft partnerships, which apparently are not going as well as they once did.
Amazon: The Wild Card
Amazon forked Android for the Kindle Fire. Its rumored phone will, on paper, have the advantages of most of the Android apps but be vertically integrated like Apple and BlackBerry. Amazon has been building up its cloud services and could offer a phone connected to them that could approach the business value proposition of BlackBerry. With its movie and music services, it could challenge the consumer advantage of Apple.Current rumors suggest Amazon will be approaching the latter opportunity first and lead with a value-priced phone with a 3D-capable screen. Amazon has showcased that it can do well on tablets -- arguably outperforming both Apple and Google in the 7-inch category but clearly lagging both Apple and Samsung in the more capable 10-inch class. This suggests that when it comes to phablets -- smartphones with 5.5-inch or larger screens -- Amazon could dominate this class, and the market could shift toward it. That's a lot of "ifs," though.
Amazon is untested with carriers, and its best move -- given its heavy cloud services capabilities -- would be an MVNO approach: buying and selling connectivity services wholesale, thus underpricing similar products sold directly through the major carriers. While Apple demonstrated that it was possible to enter the phone market and do well against the entrenched vendors, Samsung in particular has showcased that it isn't that easy anymore. Amazon will likely have a much bigger fight than Apple did as a result.
Wrapping Up: BlackBerry Has the Edge
This is a market that is clearly in flux. Apple's CEO appears to be anticipating his own departure, and a replacement could either make things better or much worse. Given history, the smart money is on the latter.Samsung and Google could kiss and make up, and the fact that Google used Samsung's troubled S4 at its I/O conference could indicate that these two either have done so or soon will.
As for the contenders, Microsoft could either bring out its own phones, repeating the Zune mistake and crippling Nokia, or it could put more of its war chest behind Nokia's effort, better ensuring its success. A major security problem could easily cause corporations to ban Android and shift back to a BlackBerry-only model, or BlackBerry could be acquired -- and mergers of this scale rarely go well.
In short, while I think BlackBerry has the edge, there are a lot of balls in the air here, and it is still almost anyone's game. Even a new player like Amazon could end up cornering the U.S. market. The only thing certain is that it will be an exciting year.
BlackBerry has three sustaining advantages: 1) It is the only firm that does keyboards well; 2) it is still the favorite when businesses buy the phones; and 3) businesses buy the phones in emerging markets. All three of these advantages are showcased in the Q5, which is basically a reduced-cost version of the Q10.
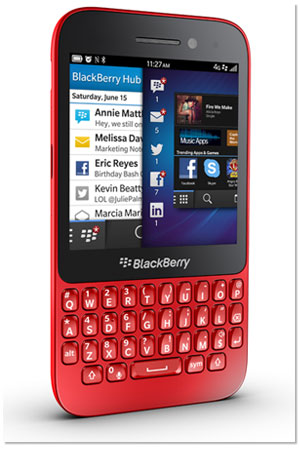
The BlackBerry Q5
It has the same features and same battery life. It has an LED rather than AMOLED screen, and a plastic case instead of black stainless steel and carbon fiber. This makes this new phone ideal for business buyers in emerging markets -- BlackBerry's strongest segment.
In addition, Alicia Keys pointed out that 56 percent of BlackBerry customers are women, and this product comes in colors and appears to have a more female-focused form, suggesting she has had some impact on the design. Keys is tightly focused on helping BlackBerry better understand the needs of its female-dominant customer base.
I'm a big fan of the Q10, and I've been carrying it for a bit. There really is nothing like a keyboard phone if you are doing email or trying to get work done, and I still favor it over a screen phone for productivity.
BlackBerry has created a phone that targets and strengthens its strongest and most loyal customer segment at a time when most phone makers don't seem to really know who their major customers are. Though it is not available in the U.S., from a standpoint of customer targeting, the Q5 is one of the most intelligent smartphones I've seen from anyone in some time, so it is my product of the week.
Thursday 9 May 2013
Advanced Cyber Attack Tools Seen Available to Hackers
Advanced cyber attack tools have become readily available for use by foreign governments and terrorists to infiltrate or cripple U.S. computer networks, two federal law enforcement officials told a congressional panel.
Dozens of countries now have sophisticated cyber espionage capabilities and terrorists want to “digitally sabotage” U.S. power grids or water supply networks, Joseph Demarest, assistant director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s cyber division, said in prepared testimony for a Senate hearing today.
U.S. Attorney for the Western District of Washington Jenny Durkan said that U.S. intelligence agencies have concluded that China and Russia are responsible for electronic intrusions into U.S. computer networks and the theft of intellectual property. Photographer: Stephen Morton/Bloomberg
“The tools and expertise to perpetrate a cyber attack with physical effects are readily available for purchase or hire,” he said.
President Barack Obama and intelligence officials have said one of their top policy priorities is preventing cyber attacks that could disrupt banks, telecommunications networks, utilities or other vital services. Lawmakers have renewed their efforts to advance cybersecurity legislation after Congress failed last year to pass a bill. The Senate Judiciary Subcommittee on Crime and Terrorism is holding a hearing today on how the government and private sector are responding to cyber threats.
The advanced cyber tools that Symantec Inc. has found recently being used for attacks include large scale data breaches that last year exposed about 93 million identities, “watering hole attacks” that target visitors to legitimate websites and the use of an estimated 3.4 million bot zombies around the world last year, according to the testimony of Cheri McGuire, Symantec’s vice president for global affairs and cyber-security policy.
Growing Threat
Cybersecurity threats posed by foreign governments and terrorist groups against U.S. networks are growing, Jenny Durkan, U.S. Attorney for the Western District of Washington, said in prepared testimony for the hearing.
Slideshow: Top Ten Hacking Countries
“Although to date they have resembled in some ways the crimes perpetrated by financially motivated criminals, their emergence and evolution make the threat of cyber-generated physical attacks, like those that might disrupt the power grid, appear no longer to be the stuff of science fiction,” she said.
To help prevent attacks, the Justice Department is establishing cells of cybersecurity specialists “to focus on particular high-priority cyber targets,” Durkan said. She said one cell is operational, without providing details.
There’s been “an uptick” in cyber attacks against U.S. electric companies this year, Carl Herberger, a vice president for the network security firm Radware Ltd. (RDWR), said in a phone interview.
Information-technology systems at three different electric companies were temporarily knocked off-line by cyber-attacks this year, said Herberger, whose company is based in Tel-Aviv with offices in New Jersey. He declined to discuss specifics or name the companies.
Legislation Introduced
“We are being out-gunned,” he said. “The trade of malicious and nefarious tools and techniques is at an ever-increasing high point and has tipped in favor of the perpetrator.”
U.S. intelligence agencies have concluded that groups in China and Russia are responsible for electronic intrusions into U.S. computer networks and the theft of intellectual property, Durkan said.
A bipartisan group of senators introduced a bill yesterday that would require the Obama administration to identify foreign countries that steal U.S. trade secrets, as well as possible actions to punish them, including blocking imports of products from companies that benefit from the theft.
The bill, which didn’t have a number, was introduced by Michigan Democrat Carl Levin, chairman of the Senate Armed Services Committee, and West Virginia Democrat Jay Rockefeller, chairman of the Senate Commerce Committee, along with Arizona RepublicanJohn McCain and Oklahoma Republican Tom Coburn.
“We need to call out those who are responsible for cyber theft and empower the president to hit the thieves where it hurts most -- in their wallets, by blocking imports of products or from companies that benefit from this theft,” Levin said.
To contact the reporter on this story: Chris Strohm in Washington at cstrohm1@bloomberg.net
To contact the editor responsible for this story: Bernard Kohn at bkohn2@bloomberg.net
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

